The Baboon
The most widely distributed baboon species and the only one to be found in Uganda is the olive baboon (Papio anubis), also known as the Anubis baboon.
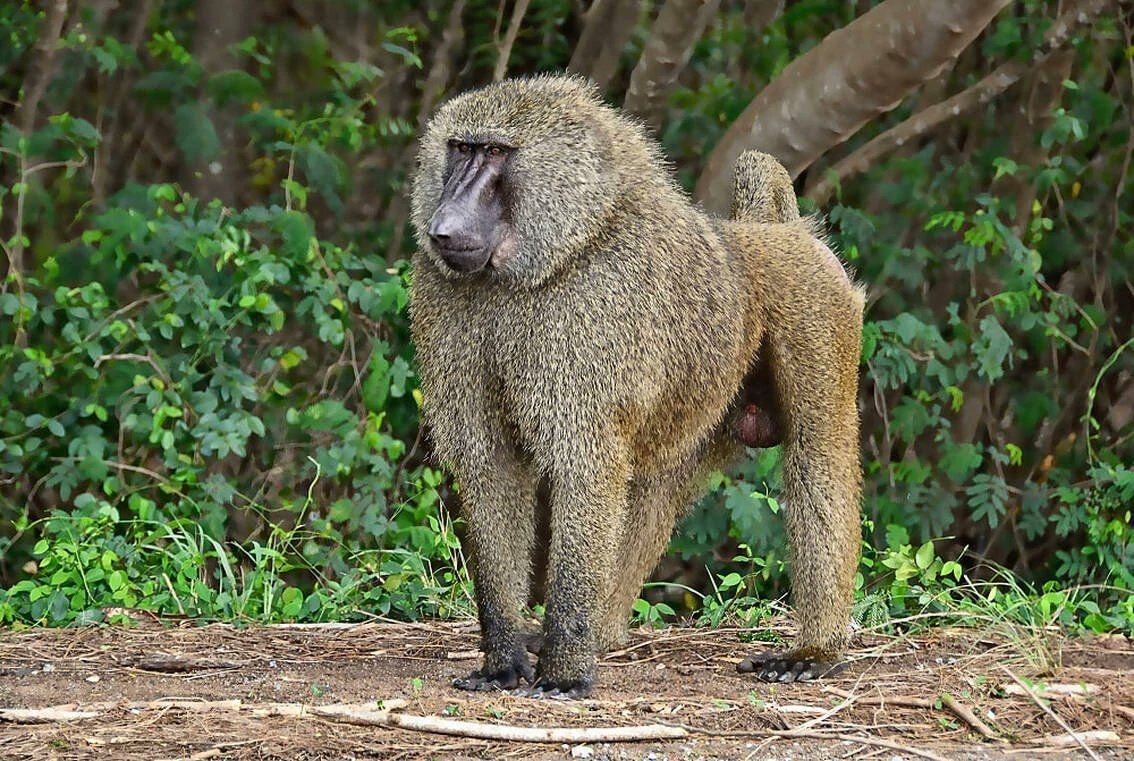

The baboon lacks a prehensile (gripping) tail, like other Old World monkeys, so it cannot use its tail as a hand but can still climb when necessary.
Baboons have long, canine-like muzzles, powerful, heavy jaws with sharp teeth, close-set eyes, thick fur other than on their muzzles, short tails, and ischial callosities, which are nerveless, hairless pads of skin on their protruding buttocks that provide comfort while sitting. Large white manes can be seen on the male hamadryas baboons. Baboons differ in size, colour, and/or the development of their canine teeth based on their gender.
Behaviour of Baboons
Baboons typically travel in packs of 50 animals, though this number can range from 5 to 250 depending on the species, region, and season. Typically, their groups contain seven or eight males, twice as many females, and the young.
The social structure of the troop is centred around the family unit of females and children. When they reach adulthood, males leave their birth troop in search of or create the groups that are most appropriate for them.
Reproduction and health of baboons.
Depending on the troop's social structure, baboon mating behaviour varies greatly. In general, each male is free to mate with any female; the males are mated in a certain order according to their social standing. After six months of pregnancy, females typically give birth to one child. Although several females may share the responsibilities for all of their offspring, the females are typically the ones who take care of the young. After roughly a year, the offspring are weaned. They mature sexually between the ages of five and eight. While the majority of females remain in the same group throughout their lives, males typically leave their birth group before reaching sexual maturity. Baboons can live up to 45 years in captivity, but in the wild, they typically only live 20 to 30 years.
Baboon Diet
Baboons are omnivorous, extremely adoptive monkeys that will consume nearly any edible object. It eats a lot of grass and leaves and hunts for berries, blossoms, seeds, pods, roots, bark, and sap from different plants.
In addition to eating primarily plants, they also consume insects and small amounts of meat from animals like hares, vervet monkeys, birds, fish, and small antelopes.
Where can I see baboons in Uganda
There are baboons all over Uganda, with the exception of the three mountain national parks. In other parts of the country, they are frequently spotted along the edges of forest preserves and even by the side of the road.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0